Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
Google Scholar citation report
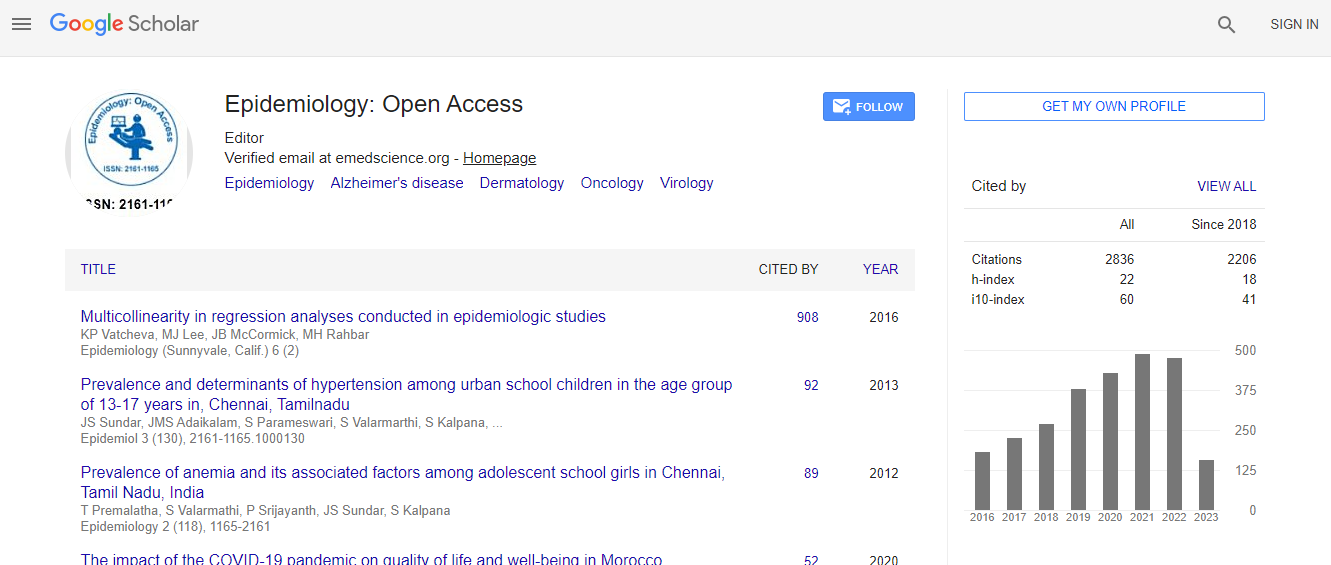
Citations : 3864
Epidemiology: Open Access received 3864 citations as per Google Scholar report
Epidemiology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Genamics JournalSeek
- SafetyLit
- Access to Global Online Research in Agriculture (AGORA)
- Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International (CABI)
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- CABI full text
- Cab direct
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Editorial Board
Submit Manuscript
Journal Impact Factor 10.58*
; 1.746* (5 Year Journal Impact Factor)
Submit manuscript at or send as an e-mail attachment to the Editorial Office at manuscript@omicsonline.org
If you are interested in publishing with us or have any questions, please feel free to contact us directly on WhatsApp .
Table of Contents
About the Journal
Index Copernicus Value 2015: 83.35
Epidemiology: Open Access (Epidemiology (Sunnyvale)) is a Peer Reviewed Journal that includes a wide range of topics in this discipline including studies on various epidemic diseases using methods like supervision, monitoring, statistical inference, analytic researches and experiments and creates a platform for the authors to make contribute towards the journal. The editorial office promises peer reviewing of the submitted manuscripts to maintain quality.Epidemiology: Open Access is a scholarly publishing that aims to publish the most complete and reliable source of information on discoveries and current developments in the form of original articles, review articles, case reports, short communications, etc. in all areas of the field, making them available online to the researchers worldwide without any subscriptions.Epidemiology (Sunnyvale) is using Editorial Tracking System to maintain quality in the online manuscript submission, review and tracking systems. Editorial board members of Epidemiology (Sunnyvale) or outside experts conduct the review; at least two independent reviewer’s approval followed by the editor is required for the acceptance of any citable manuscript.OMICS International organizes 700+ conferences every year across USA, Europe & Asia in association with more than 1000 scientific societies and publishes 1000+ scholarly open access journals which contain over 50000 eminent reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Submit manuscript at https://www.scholarscentral.org/submissions/epidemiology-open-access.html or send as an e-mail attachment to the Editorial Office at manuscript@omicsonline.org
Reproductive Epidemiology
Epidemiology studies the sexual disease and disorders caused in men and women in a certain population. These study results can be used to analyse the cause of a medical condition and how it can be prevented, prevalence in a population and the urgency with which it needs to be addressed.
Reproductive Epidemiology investigates the distribution and determinants of reproductive diseases in human populations. Epidemiologic skills can be used to better understand the cause of a medical condition and how it can be prevented, or its prevalence in a population and the urgency with which it needs to be addressed.
Reproductive topics include pubertal development, gynecologic disorders, female reproductive cancers, sexually transmitted infections, menstruation, menopause, female and male fertility, and assisted reproductive technologies.
Related Journals of Reproductive Epidemiology
International of journal of epidemiology, Reproductive Health, Reproductive Health Matters, Reproduction, Clinical and Experimental Reproductive Medicine, European Journal of Contraception and Reproductive Health Care
Nutrition Epidemiology
Nutrition epidemiology is a branch that is specialized in research to examine the role of nutrition played in the cause of diseases. To monitor the nutrition status in a population and to develop new interventions to reach the healthy eating patterns in the population.
The effects of dietary intake and nutritional status on health are complex. Multiple nutrients work together in the body, with differing impacts on different systems and under differing environmental conditions. The effects of dietary intake may be modified or confounded by other exposures, including physical activity, smoking, and alcohol consumption.
Understanding and untangling specific effects requires an understanding of the complex interactions among exposures and the technical skills for clarifying them in population-based data. Epidemiologic studies may generate important new ideas about health risks or protective factors, and offer suggestions for public health policy.
Related Journals of Nutrition Epidemiology
Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, European Journal of Nutrition, International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research, Journal of Nutrition, Health and Aging, Journal of Nutrition and Health, Advances in nutrition (Bethesda, Md.)
Emerging Infection
Emerging infection is the infectious disease that has increased rapidly compared to the past condition and tends to increase in the future. Emerging infectious diseases range 12% of all the total deadly pathogens which can cause fatal effects.
Emerging infections are caused by newly identified species or strains of bacteria, virus, pathogens or any microbial organism that may have evolved from a known infection or spread to a new population or area undergoing ecologic transformation.
Drug resistant diseases, Nosocomial infections are emerging in hospitals, and extremely problematic. Emerging infections are of growing concern. Adverse synergistic interactions between emerging diseases and other infectious and non-infectious conditions leads to the development of novel syndemics.
Related Journals of Emerging Infection
Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, Hospital Infection Control, Infection, American Journal of Infection Control, Epidemiology and Infection, Journal of Infection and Public Health
Environmental Epidemiology
Environmental epidemiology is a branch of epidemiology concerned with the discovery of the role played by environment towards protections from injuries, illnesses, growth disorders, disabilities, and death. Environmental epidemiology studies external factors that affect the incidence, prevalence, and geographic range of health conditions.
Environmental epidemiology identifies and quantifies exposures to environmental contaminants; conducts risk assessments and risk communication; provides surveillance for adverse health effects; and provides health-based guidance on levels of exposure to such contaminants.
Environmental epidemiology seeks to understand how physical, chemical, biologic, as well as, social and economic factors affect human health. Social factors, that is where one lives, works, socializes or buys food, often influence exposure to environmental factors.
Environmental epidemiology research can inform risk assessments; development of standards and other risk management activities; and estimates of the co-benefits and co-harms of policies designed to reduce global environment change, including policies implemented in other sectors (e.g. food and water) that can affect human health.
Related Journals of Environmental Epidemiology
Epidemiology & Community Health, Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene, Environmental Sciences: Processes and Impacts, Occupational and Environmental Medicine, International Journal of Occupational Medicine and Environmental Health
Trends in Maternal Mortality
Death of women caused by pregnancy or its related medication or due to termination of pregnancy or duration or site of pregnancy is known to be maternal mortality.
Trends in maternal mortality includes various conditions which can lead to maternal mortality. There are significant maternal mortality intracountry variations, especially in nations with large equality gaps in income and education and high healthcare disparities.
Women living in rural areas experience higher maternal mortality than women living in urban and suburban centers because those living in wealthier households, having higher education, or living in urban areas, have higher use of healthcare services than their poorer, less-educated, or rural counterparts. There are also racial and ethnic disparities in maternal health outcomes which increases maternal mortality in marginalized groups.
Related Journals of Trends in Maternal Mortality
Molecular Epidemiology, MMWR. Recommendations and reports : Morbidity and mortality weekly report. Recommendations and reports / Centers for Disease Control, MMWR. Surveillance summaries : Morbidity and mortality weekly report. Surveillance summaries / CDC, MMWR. Morbidity and mortality weekly report,
Primary Care Epidemiology
Primarycare epidemiology can contribute to wider improvements in health and healthcare services, through better understanding of disease aetiology, use of healthcare services and the role of different healthcare interventions.
Typically this provider acts as the first contact and principal point of continuing care for patients within a health care system, and coordinates other specialist care that the patient may need. Patients commonly receive primary care from professionals such as a primary care physician, a nurse practitioner, or a physician assistant. In some localities such a professional may be a registered nurse, a pharmacist, a clinical officer, or a Ayurvedic or other traditional medicine professional.
Related Journals of Primary Care Epidemiology
Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention, Primary health care research & development, Primary Care Respiratory Journal, Primary Care Diabetes, Quality in Primary Care, Journal of Primary Health Care
Intestinal Epidemiology
Intestinal epidemiology deals with the proper intestines, intestinal diseases, intestinal disorders, and various health issues people face. Understanding these disease conditions in a population can make it possible to invent remedies and prevention strategies.
In human anatomy, the intestine is the segment of the alimentary canal extending from the mouth via stomach to the anus. In humans and other mammals, consists of two segments, the small intestine and the large intestine. In humans, the small intestine is further subdivided into the duodenum, jejunum and ileum while the large intestine is subdivided into the caecum and colon.
Intestinal epidemiolgy studies help to analyse and understand intestinal diseases involving the gastrointestinal tract, namely the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum, and the accessory organs of digestions, the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
Related Journals of Intestinal Epidemiology
Cancer Epidemiology, Journal of Gastroenterology, Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer, Gastroenterology Research and Practice, Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology
Renal Epidemiology
Epidemiology of renal system includes disease conditions of kidneys such as kidney stones, nephritis, chronic and acute kidney diseases, gallbladder stones, urinary tract infections and all the other disease conditions. By studying and understanding renal epidemiology the proper prevention measures can be taken.
According to survey conducted chronic kidney disease resulted in 956,000 deaths in 2013 up from 409,000 deaths in 1990.In many patients, previous renal disease or other underlying diseases are already known. A significant number present with chronic kidney disease of unknown cause. In these patients, a cause is occasionally identified retrospectively.
Related Journals of Renal Epidemiology
Epidemiology & Community Health, Journal of Renal Care, Journal of Renal Nutrition, Renal Failure, Renal Society of Australia Journal
Etiology
Etiology is the study of cause or origin. In epidemiology etiology plays a vital role to understand the origin and cause of the disease. By studying the etiological conditions of infectious diseases, communicable and non-communicable diseases its cure and prevention can be intervened.
Etiology refers to the many factors coming together to cause an illness. It is normally the focus of epidemiological studies.
Related Journals of Etiology
Cancer Epidemiology, Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention, International Journal of Epidemiology, Clinical Epidemiology, Epidemiologia e prevenzione
Epidemiology and Biostatistics
Epidemiology and biostatistics are the two branches of science that deals with the study of etiological conditions of a particular disease or health condition and present statistics of the condition in a given population or given community.
Epidemiology is the science that studies the patterns, causes, and effects of health and disease conditions in defined populations. It is the cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidence-based practice by identifying risk factors for disease and targets for preventive healthcare.
Epidemiologists rely on other scientific disciplines like biology to better understand disease processes, statistics to make efficient use of the data and draw appropriate conclusions, social sciences to understand proximate and distal causes better, and engineering for exposure assessment.
Biostatistics (or biometry) is the application of statistics to a wide range of topics in biology.
Related Journals of Epidemiology and Biostatistics
Ecology and epidemiology Journal, National health statistics reports, National vital statistics reports, Vital and health statistics
Epidemiology of Tuberculosis
Epidemiology of tuberculosis is the study about causative organism Mycobacterium tuberculosis and its pathophysiology, tuberculosis occurence, routes of transmission from one person to other, the effective treatments available and further precautions to be taken to avoid reversion of the disease.
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria usually attack the lungs, but TB bacteria can attack any part of the body such as the kidney, spine, and brain, which most commonly affects the lungs. It is transmitted from person to person via droplets from the throat and lungs of people with the active respiratory disease. In healthy people, infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis often causes no symptoms, since the person's immune system acts to “wall off” the bacteria.
The symptoms of active TB of the lung are coughing, sometimes with sputum or blood, chest pains, weakness, weight loss, fever and night sweats. Tuberculosis is treatable with a six-month course of antibiotics.
Related Journals of Epidemiology of Tuberculosis
International of journal of epidemiology, Current Research in Tuberculosis, Indian Journal of Tuberculosis, International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases
Epidemiology and Infection
Epidemiology is the occurrence of communicable and chronic diseases, principally in the form of epidemics which is caused by microbial infection. Infection is the invasion of foreign microbial organism on our immune system for its survival and growth.
Infections are caused by infectious microrganisms including viruses, viroids, prions, bacteria, parasitic roundworms and pinworms, ticks, mites, fleas, and lice, ringworm, and other macroparasites such as tapeworms and other helminths. According to epidemiologic studies by WHO the top three single agent/disease killers are HIV/AIDS, TB and malaria.
While the number of deaths due to nearly every disease have decreased, deaths due to HIV/AIDS have increased fourfold. Childhood diseases include pertussis, poliomyelitis, diphtheria, measles and tetanus. Children also make up a large percentage of lower respiratory and diarrheal deaths.
Related Journals of Epidemiology and Infection
Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, Epidemiology and Infection, Hospital Infection Control, Journal of Infection and Public Health, Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy
Disambiguation
Disambiguation is the way of clearing the ambiguous discussions and making it direct and clear to understand. Epidemiology on various health conditions provides clear idea on the condition avoiding disambiguation.
Epidemiology and Community Health
Epidemiology and community health is the wide scope which covers the epidemic and infectious diseases affecting certain area or community’s health. This not only covers their occurrence and spread but also concentrates on recurrence and prevention methods to be taken.
Community health a field of public health, is a discipline which concerns itself with the study and improvement of the health characteristics of biological communities. While the term community can be broadly defined, community health tends to focus on geographical areas rather than people with shared characteristics.
Related Journals of Epidemiology and Community Health
Community Dentistry and Oral Epidemiology, Epidemiology & Community Health, Progress in community health partnerships : research, education, and action, Family and Community Health, Indian Journal of Community Health, Journal of Community Health Nursing, Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health
Epidemiology and Disease Control
Epidemiology of disease conditions is important to control the disease. Hence epidemiology and disease control plays a vital role in the betterment of human race. Epidemiology for disease control has been increased in the recent days by using simple mathematical calculations and formulations disease control can be achieved.
Related Journals of Epidemiology and Disease Control
Journal of Epidemiology and Global Health, Vascular diseases, Breast Diseases, Diseases of the chest, Diseases of the Esophagus, Ethnicity and Disease
Global Health
Global health is the health of populations in a global context. It has been defined as "the area of study, research and practice that places a priority on improving health and achieving equity in health for all people worldwide". Problems that transcend national borders or have a global political and economic impact are often emphasized.
Henceforth, global health is regarding worldwide health improvement, reduction of differences, and protection against global threats that disregard national borders. Global health can be achieved by estimating and analysing the current disease conditions. Various statistical and prevalence studies were done on this occasion and by using the same we can take the step towards global health.
Related Journals of Global Health
Journal of Epidemiology and Global Health, Global Health Action, Global health promotion, Journal of Epidemiology and Global Health, The Lancet Global Health
Neuroepidemiology
Neuroepidemiology is the part of epidemiology with deals with the neurological disease conditions and their frequency of occurrence in a specific population. The scope of the neuroepidemiology includes incidence, prevalence, risk factors, diagnosis and prevention of the various neurological disorders.
Related Journals of Neuroepidemiology
Vaccines Epidemiology, BMC Neurology, Case Reports in Neurology, Cognitive and Behavioral Neurology, Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery, Neurology: Clinical Practice
Pediatric Epidemiology
Pediatric epidemiology is the branch of epidemiology which deals with the disorders and disease conditions that appear in the children, adolescence, and early childhood and the age limit usually ranges from birth up to 18 years of age.
A medical practitioner who specializes in this area is known as a pediatrician. Pediatrician work both in hospitals, particularly those working in its specialized subfields such as neonatology, and as primary care physicians who specialize in children.
It includes all the conditions like obesity, congenital diseases, eating disorders, and genetic disorders that inherit from the parents.
Related Journals of Pediatric Epidemiology
Molecular Epidemiology, Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine, Pediatric and Developmental Pathology, Pediatric Blood and Cancer, Pediatric Cardiology, Pediatric endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism
Behavioral Epidemiology
Behavioral epidemiology is the branch of epidemiology that is related with the psychology. In this we can study about the lifestyle and behaviors of people and how they affect their health conditions. Behavioral disease conditions and disease re-occurrence depends on the behavior is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals in conjunction with themselves or their environment, which includes the other systems or organisms around as well as physical environment.
It is the response of the system or organism to various stimuli or inputs, whether internal or external, conscious or subconscious, overt or covert, and voluntary or involuntary.
Related Journals of Behavioral Epidemiology
Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, Behavioral and Brain Sciences, Behavioral Healthcare, Cognitive and Behavioral Neurology, Integrative psychological & behavioral science, International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity
Veterinary Epidemiology
Veterinary epidemiology is principally concerned with the study of diseases or conditions in animals that affect certain population or patterns of disease conditions within a population of animals, by which they are affected, the location of affected animals, and the patterns of disease through time can be studied by veterinary epidemiology.
Veterinary science helps human health through the monitoring and control of zoonotic infectious disease transmitted from non-human animals to humans, food safety, and indirectly through human applications from basic medical research.
They also help to maintain food supply through livestock health monitoring and treatment, and mental health by keeping pets healthy and long living. Veterinary scientists often collaborate with epidemiologists, and other health or natural scientists depending on type of work. Ethically, veterinarians are usually obliged to look after animal welfare.
Related Journals of Veterinary Epidemiology
Epidemiology & Community Health, Research in Veterinary Science, Veterinary Clinical Pathology, Veterinary Medicine, Veterinary Surgery, Canadian Journal of Veterinary Research
Genetic Epidemiology
Genetic epidemiology is a branch of epidemiology which determines the role played by genetic material like DNA, RNA, in the health and disease in families and in specified populations. Heredity characters and congenital disease conditions can be studied.
Related Journals of Genetic Epidemiology
Cancer genetics, Circulation. Cardiovascular genetics, Genetics in Medicine, Twin Research and Human Genetics, Journal of Community Genetics
Cancer Epidemiology
Cancer is principally concerned with the study of cancer, its causes, detection, and treatment based on the progression of the disease. Cancer epidemiology is concerned with the estimation and study of cancer and its prevalence in a certain area of population.
Related Journals of Cancer Epidemiology
Cancer Epidemiology, Blood Cancer Journal, Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy, Cancer Control, Cancer and Chemotherapy Reviews, Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention
HIV Surveillance
HIV surveillance means observing and understanding the patterns, severity and occurrence of the HIV infection from one person to other in a population. By this surveillance studies the spread of the infection can be halted and respective measurements can be taken.
Related Journals of HIV Surveillance
AIDS Care - Psychological and Socio-Medical Aspects of AIDS/HIV, Journal of HIV/AIDS and Social Services, HIV and AIDS Review, HIV clinician / Delta Region AIDS Education & Training Center, HIV Medicine
Oral/Dental Epidemiology
Dental epidemiology studies the factors responsible for the development of common oral conditions and dental problems. The relation between dental problems and other chronic diseases can be understood.
Related Journals of Oral/Dental Epidemiology
Journal of Epidemiology, Community Dental Health, Dental implantology update, Oral health and dental management, ORAL and Implantology, Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology
Economic Epidemiology
Economic epidemiology is the union of both epidemiology and economics. Its assumption is to include incentives for healthy behavior and behavioral responses of attendants into an epidemiological context to better understand how diseases are transmitted. This helps the healthcare providers to understand how certain things influence the disease transmission.
Related Journals of Economic Epidemiology
Journal of Epidemiology and Global Health, PharmacoEconomics - Italian Research Articles, Health Economics, Journal of Medical Economics, Nursing Economics, National Bureau of Economic Research bulletin on aging and health
Epidemiology: Open Access journal is supporting 4th International Conference on Epidemiology and Public Health going to be held on June 28-30, 2016 in Bangkok, Thailand, 4th International Congress on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases going to be on May 16-18, 2016 at San Antonio, USA, 4th International Conference on HIV/AIDS, STDS and STIS going to be on October 03-05, 2016 at Miami, USA and World Congress on Public Health & Nutrition schduled on March 10-12, 2016 at Madrid, Spain.
Journal Highlights
Major Disease Statistics
*2024 Journal Impact Factor was established by dividing the number of articles published in 2022 and 2023 with the number of times they are cited in 2024 based on Google Scholar Citation Index database. If 'X' is the total number of articles published in 2022 and 2023, and 'Y' is the number of times these articles were cited in indexed journals during 2024 then, journal impact factor = Y/X
Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process (FEE-Review Process):
Epidemiology: Open Access is participating in the Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process (FEE-Review Process) with an additional prepayment of $99 apart from the regular article processing fee. Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process is a special service for the article that enables it to get a faster response in the pre-review stage from the handling editor as well as a review from the reviewer. An author can get a faster response of pre-review maximum in 3 days since submission, and a review process by the reviewer maximum in 5 days, followed by revision/publication in 2 days. If the article gets notified for revision by the handling editor, then it will take another 5 days for external review by the previous reviewer or alternative reviewer.Acceptance of manuscripts is driven entirely by handling editorial team considerations and independent peer-review, ensuring the highest standards are maintained no matter the route to regular peer-reviewed publication or a fast editorial review process. The handling editor and the article contributor are responsible for adhering to scientific standards. The article FEE-Review process of $99 will not be refunded even if the article is rejected or withdrawn for publication.
The corresponding author or institution/organization is responsible for making the manuscript FEE-Review Process payment. The additional FEE-Review Process payment covers the fast review processing and quick editorial decisions, and regular article publication covers the preparation in various formats for online publication, securing full-text inclusion in a number of permanent archives like HTML, XML, and PDF, and feeding to different indexing agencies.
h-index
Articles published in Epidemiology: Open Access have been cited by esteemed scholars and scientists all around the world. Epidemiology: Open Access has got h-index 22, which means every article in Epidemiology: Open Access has got 22 average citations.
Recently Published Articles
-
Infectious diseases Meet 2020 Awards 2020 Report
Giulio Tarro -
Dengue 2020 – Webinar –Awards
Vince Jordan -
Award for 11th International Conference on Emerging Diseases
Reza Nassiri -
Award Content for COPD 2021
Ravi Sharma -
Awards for COPD 2020
Robert Buckingham -
Epidemiology, Ethics, and the Application of Emergency Response in a Global Health Crisis
Jenny Salva

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi